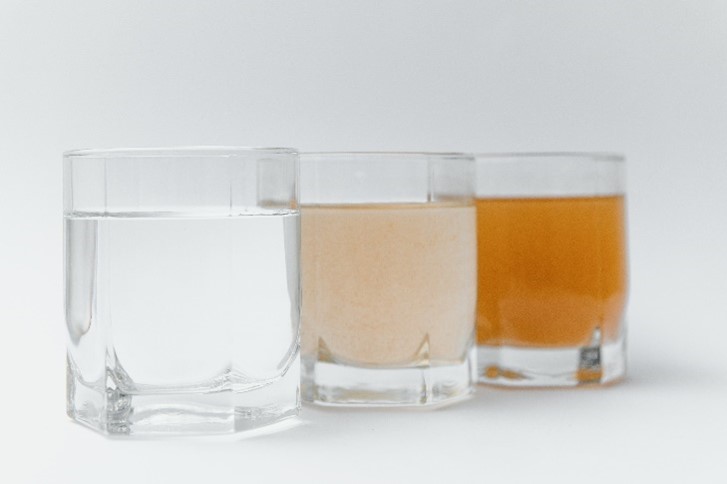
A water softener is a valuable tool for homes affected by varying levels of hard water, offering a multitude of benefits. It works by removing minerals such as calcium, iron, and magnesium, which are primarily responsible for hard water issues. The use of a water softener helps avoid problems like mineral deposits, scale buildup that can lead to leaky faucets and clogged pipes, damage to appliances using water, residues on dishes cleaned in dishwashers, dry skin and hair post-showering, and the fading of clothes washed in hard water.
By eliminating these heavy minerals, softened water enhances the quality of life in several ways:
- improved skin and hair health
- brighter and softer laundry
- cleaner dishes and glasses
- reduced cleaning effort
- long-term cost savings
- improved taste and clarity of drinking water.
How a Water Softener Works
The core technology behind most water softeners is the ion exchange process, which replaces hard minerals with sodium (or sometimes potassium). This process occurs as water flows through a tank filled with resin beads that are pre-saturated with sodium. The hard minerals swap places with sodium ions, which then dissolve into the water, leaving it softened. Eventually, the resin beads get saturated with the removed minerals and need to be regenerated with sodium-rich water to restore their softening capability, allowing the system to continue providing softened water to the household.
Types of Water Softeners
Water softeners are designed to address hard water issues through two primary methods: ion exchange, which removes heavy minerals from the water, and neutralization, which prevents these minerals from clustering and keeps them dissolved in the water. The two main categories of water softeners, each functioning differently, include:
- Salt-based systems, which may also include dual-tank configurations
- Salt-free systems, which include magnetic variants
Salt-based water softeners are widely used for their effectiveness in removing minerals like calcium and magnesium from water and exchanging them for sodium. This process turns hard water soft, making it healthier for use. Despite their efficiency, these systems require weekly salt recharges and are larger, which may not suit smaller spaces. However, portable versions are available, ideal for RVs, boats, and small homes, offering an affordable solution for on-the-go soft water needs. These portable softeners are less expensive but need frequent recharging. While salt-based softeners slightly increase the water’s sodium content, they remain within a safe range for most people, though those on low-sodium diets might prefer alternatives.
Dual-Tank Water Softeners
Dual-tank water softeners feature two resin tanks, ensuring a constant supply of soft water, even during one tank’s regeneration phase. They’re especially beneficial for well water, capable of filtering heavy minerals more effectively. However, dual-tank systems are larger, more expensive, and not necessary for most households, but they excel in high-demand situations without the risk of running out of softened water.
Salt-free water softeners, unlike their salt-based counterparts, do not remove hard minerals from water but instead, condition the water to prevent these minerals from forming scale on fixtures and appliances. They are an initial costlier option that operates without salt or electricity, suitable for small to large homes. However, they may not perform as well in areas with extremely hard water or high water usage.
Electromagnetic and Magnetic
Electromagnetic and magnetic water softeners are compact, making them ideal for small spaces. They work by altering the charge of mineral ions with a magnetic field, preventing them from sticking to surfaces. Electromagnetic models require an electrical outlet, while magnetic ones do not, offering a maintenance-free solution albeit with limited effectiveness for smaller homes.
Polyphosphates
Polyphosphate softeners use a filtration cartridge to condition water, preventing scale formation, and are commonly used in commercial settings to protect equipment. Full filtration systems not only prevent scaling but also remove a wide range of contaminants, making water safer but requiring periodic and costly filter replacements.
Full Filtration
Full filtration systems offer a dual benefit: they soften water and eliminate a variety of drinking water contaminants. Operating without salt, these systems utilize a filtration process that transforms minerals into a crystalline form to prevent scale buildup on pipes and appliances. Additionally, they effectively filter out harmful substances such as herbicides, bacteria, viruses, pesticides, and chlorine. While offering significant advantages, the filters in these systems come with a higher cost and need replacement approximately every six months to a year.
It’s crucial to recognize the distinction between water softeners and purifiers. Water softeners are safe for treating water with hardening minerals, either by removing or neutralizing them to prevent them from causing scale. However, they do not function as water filters and are incapable of eliminating other harmful substances from the water. Therefore, their use should be limited to softening water. For concerns about the overall safety of your drinking water, especially regarding contaminants other than hardening minerals, it’s advisable to consult your local health department, conduct personal tests, or have the water professionally analyzed.
Not sure what’s right for your home or business? Contact the experts at Reynolds Water Conditioning; we’ll walk you through the process to determine the best solution for your water type.
Reynolds Water Conditioning was established in 1931 and is Michigan’s oldest water conditioning treatment company. Still owned and operated by the Reynolds family, we take pride in providing the highest quality products at a cost-effective price. If your tap water lacks the quality you deserve, contact us today at 800-572-9575.
Written by the digital marketing team at Creative Programs & Systems: www.cpsmi.com